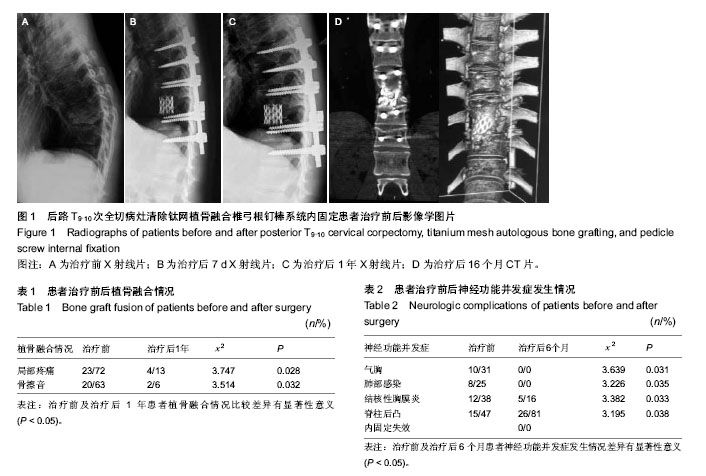
| [1] Faciszewski T, Winter RB, Lonstein JE, et al. The surgical and medical perioperative complications of anterior spinal fusion surgery in the thoracic and lumbar spine in adults. A review of 1223 procedures. Spine. 1995;20:1592-1599.
[2] Wang B,Ozawa H,Tanaka Y,et al.One-stage lateral rhachotomy and posterior spinal fusion with compression hooks for Pott’s paralysis in the elderly. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006;14(3):310-314.
[3] 兰香谋.脊柱结核外科手术进展[J].黑龙江医药,2012, 25(3): 468-469.
[4] 董翔宇,申才良.脊柱结核治疗方法研究进展[J].安徽医药,2012, 16(7):882-883.
[5] Zhang HQ, Huang S, Guo HB, et al. A clinical study of internal fixation, debridement and interbody thoracic fusion to treat thoracic tuberculosis via posterior approach only. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(2): 293-298.
[6] Oga M,Arizono T,Takasita M,et al.Evalution of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis: clinical and biologic study. Spine. 1993;18(13):1890-1894.
[7] 周劲松,陈建庭,金大地,等.结核分枝杆菌对材料粘附能力的体外实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2003,13(11):670-673.
[8] Ha KY,Chang YG,Ryoo SJ. Adherence and biofilm formation of staphylococcus epidermidis and mycobaecterium tuberculosis on various spinal implants. Spine. 2005;30(1):38-43.
[9] 郑建平,肖青峰,廉凯,等.前路病灶清除、钛网充填植骨及内固定治疗胸腰椎结核[J].医学综述,2013,19(4):728-730.
[10] 王冰,吕国华,马泽民,等.前路病灶清除、钛网植骨融合及内固定治疗胸腰椎结核[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(12):724-727.
[11] 张浩,申国庆,高发旺,等.前路一期病灶清除植骨内固定治疗胸椎及胸腰段脊柱结核并不全瘫[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(02): 139-140.
[12] 程小翠,娄湘红.前后路一期手术治疗多节段胸椎结核并截瘫23例围术期护理[J].齐鲁护理杂志,2010,16(26):66-67.
[13] 郝敬旺,王坤正,杨吉春,等.一期后路内固定前路病灶清除植骨融合术治疗胸腰段脊柱结核[J].临床骨科杂志,2012, 15(5): 508-510.
[14] 詹新立,肖增明,贺茂林,等.前方经胸骨或侧前方经肩胛下入路手术治疗上胸椎结核[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(11): 808-812.
[15] 刘建文,宋应超,李振武,等.肩胛下经胸前路病灶清除减压植骨内固定治疗上胸椎结核并截瘫[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004, 14(12): 757-759.
[16] 姜世平,何健飞,蒋兴粒,等.一期手术内固定治疗胸腰脊柱结核[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2005,26,(4):268-269.
[17] 康锦,贾卫斗,张英魁,等.后路植骨短节段内固定同期病灶清除治疗脊柱结核[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2001,8(6):614-616.
[18] 邓幼文,吕国华,王冰,等.一期后路VCR技术治疗活动期胸腰段脊柱结核伴严重后凸畸形[J].中南大学学报, 2008,33(9): 865-870.
[19] 王亚平,王新春,熊才亮,等.经后路同一切口侧前方病灶清除植骨内固定术治疗胸椎结核[J].重庆医学,2013,42(30): 3686-3686.
[20] 陈宣维,林建华,陈雷,等.一期后路病灶清除植骨融合内固定治疗胸椎结核[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(10):1172-1175.
[21] 姜传杰,杨永军,谭远超,等. 一期后路病灶清除椎体钉内固定治疗中上胸椎结核[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(4):326-330.
[22] 曹秦辉,李永民,王旭.一期前路病灶清除加钛网植骨钢板内固定治疗胸椎结核[J].河北医药,2012,34(11):1685-1686.
[23] 张轶群,李时中,尹建文,等.经肋横突一期病灶清除钛网植骨融合内固定治疗胸椎结核[J].中外医疗,2011,(12):46-48.
[24] 林慰光,胡奕山,郑干轩,等.后路椎体次全切除和钛网加钉棒重建术的生物力学研究术[J].广东医学,2012,33(19):2878-2880.
[25] 黄世敏,林明侠.钛网植骨联合颈前路钢板内固定术治疗颈椎病的临床护理[J].护士进修杂志,2012,27(1):53-54.
[26] 宾永焰,田乃宜,郭义城,等.一期前路病灶清除钛网植骨后路内固定治疗胸腰椎结核并后凸畸形66例疗效观察[J].临床军医杂志, 2014,42(5):466-468.
[27] 王国新,邓海涛,符江.前路减压钛网植骨内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折疗效观察[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(3):256-258.
[28] 郑智祥. 前路椎体次全切钛网植骨钢板内固定术治疗42例颈椎病的临床疗效分析[J].吉林医学,2011,35 (18):3832-3933.
[29] 侯力强,李建军,冷燕奎,等.后路椎体次全切钛网植骨重建治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14 (1):22-24.
[30] 胡资兵,曾荣,孙欣,等.改良一期后入路术式治疗胸椎结核的临床分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22 (17):1584-1588.
[31] 王明贵,饶锐强,王海.不同手术方式治疗老年胸椎结核的效果比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(15):4127-4129.
[32] 费骏,赖震,石仕元,等.两种术式治疗胸椎结核的对照研究[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2013,23 (3):202-204.
[33] 刘锐.两种手术治疗胸椎结核临床分析[J].海南医学院学报,2012, 18(3):378-380,383.
[34] 王福兵,马大年.28 例胸腰段脊柱结核合并截瘫的外科治疗体会[J].实用临床医药杂志,2011,15(7):110-111.
[35] 杨俊,赵敏,周江军,等.Ⅰ期后路病灶清除椎弓根内固定钛笼椎间植骨持续冲洗引流治疗胸椎结核[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(5):393-395.
[36] 赵敏,张立,许建中,等. 一期后路病灶清除、椎体间钛笼植骨椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸椎结核[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(3): 251-255.
[37] 朱定川,高峰,曾建成.胸椎结核经前路病灶清除融合单钉棒固定术的疗效观察[J].华西医学,2014,29(1):26-29.
[38] 冯华明,黄笃,康照利,等.前路病灶清除植骨及内固定治疗胸腰椎结核疗效分析[J].中国医药导报,2011, 8(1):155-159.
[39] 宋玉光,江伟,叶蜀新,等.一期前路病灶清除植骨单钉棒内固定治疗多发胸椎结核[J].中国医药指南,2013, 11(1):412-413.
[40] 张学良,王文已.一期后路内固定病灶清除植骨融合治疗上胸椎结核[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2014, 20(6):481-483, 503.
[41] Gao Z, Wang M, Zhu W, et al. Tuberculosis of ultralong segmental thoracic and lumbar vertebrae treated by posterior fixation and cleaning of the infection center through a cross-window. Spine J. 2014. pii: S1529-9430(14)00656-1. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.06.025. [Epub ahead of print] |